Permeability
Permeability is a parameter that is defined on how smooth or easy a fluid flows through a porous media.
This physical property was defined by Darcy, and that is the origin of the name of the units that are used for permeability values.
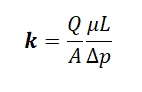
- Where:
- Q/A= Darcy velocity = flow rate Q over unit of cross area to flow A
- k= absolute permeability
- µ= viscosity
- p= pressure
Permeability has been used as a cut-off parameter to diferentiate between conventioanl and unconventional reservoirs, but this will depend on the fluid type that is going to be produced (oil or gas).
Generally, permeabilidad is calculated through lab methods, where a rock sample is tested with different techniques that measure how easy a fluid moves through the pores of the rocks. However, these measurements tend to be unprecised due to rocks conditions after they have been extracted from the wellbore, which are in some cases very different that the original conditions.
There are different equations that have been created by diverse authors to calculate permeability, but lab measurements have not been not replaced by them.
Also, there are permeability measurements derived from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) well logs, and some oil services companies offer also effective porosity values through these well logs, which are estimated from the hydrogen content that is measured from the rock pores.
It will depen on the petrophycist or reservoir criteria which values are going to be used to make estimatation, if from lab data or from values derived from equations.
Like in other sections of the blog, the permeability equations can be found at the navegation bar above:
You can calculate the following Permeability Equations:

No comments:
Post a Comment