Water Saturation (Sw)- Dewan (1983) - Dispersed Clay Model
Dewan (1983) also created an equation for the calculation of water saturation for dispersed clay models. This equation includes values such as water and true formation resistivities, sonic derived porosity, and a constant "q" that depends on the density and sonic derived porosity. The expression is the following:
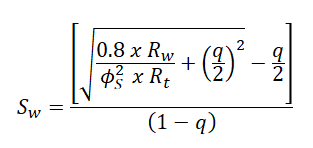
- Where:
- Sw= water saturation of the uninvaded zone
- Rt= true formation resistivity (i.e., deep induction or deep laterolog corrected for invasion)
- Rw= resistivity of formation water at formation temperature
- ɸs= sonic porosity
- q= intergranular space filled with clay
| Calculate Water Saturation (Sw) - Dispersed Clay Model- Dewan (1983) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Constant q (intergranular space filled with clay)
Constant q is related to the intergranular space filled with clay, and this depends on the values of density and sonic porosity. The equation to calculate it, is the following:
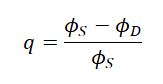
- Where:
- ɸD= density porosity
- ɸs= sonic porosity
- q= intergranular space filled with clay
| Calculate Constant q | |||
|---|---|---|---|

No comments:
Post a Comment